
The book 'Outside In' by the Forrester researchers Manning and Bodine, links the work of several Customer Experience (CX) giants over the decades: From Deming to Parasuraman to Peppers to Reichheld to Forrester.
As we should expect, I believe each of these thinkers have contributed their insights and advice in context; they are products of their time and the state of the technology and marketplace.
The insight came when I saw again the 3 tiered customer experience pyramid modified slightly by Forrester.
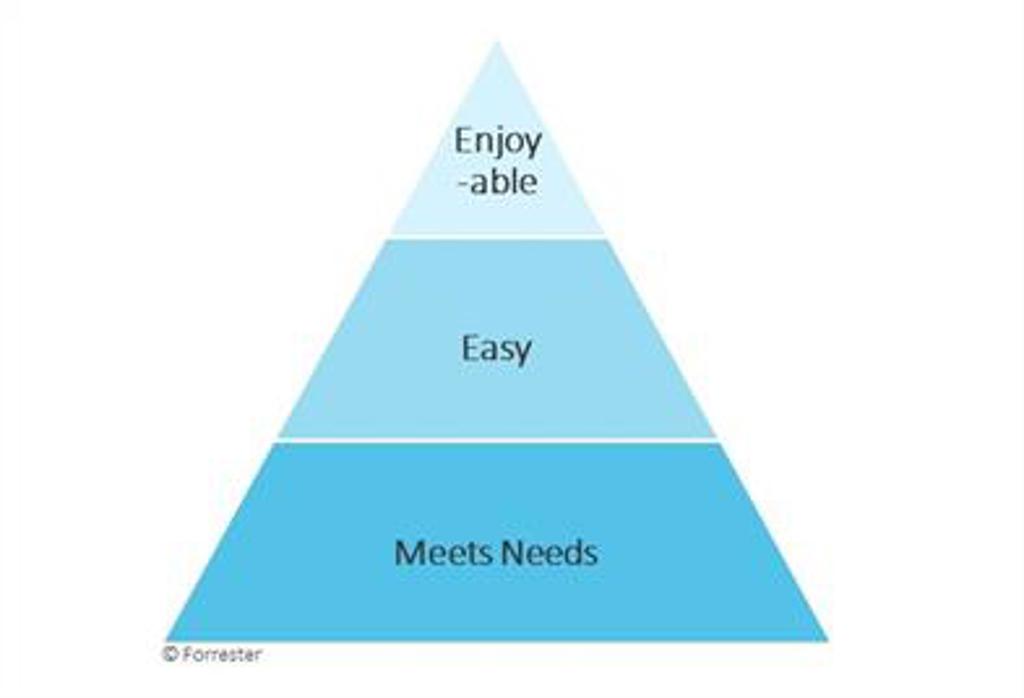
Delivering a consistently good customer experience requires the execution of a hierarchy of sequenced requirements, analogous to Maslow's hierarchy of needs in that each level must be satisfied before the next becomes important. An intelligently personalised email cannot make up for lack of stock, and a friendly call centre agent cannot make up for a regularly incorrect credit card statement
Delivering the type of customer experience that will lead to customer loyalty in a competitive market now requires that organisations pay attention to their performance on all three levels. Companies get loyalty returns by optimising at each level and you cannot skip levels.
Meeting Customer Needs
W.E. Deming developed the principles for what became Total Quality Management (TQM) during the 1950s in Japan. This was a time when manufacturing was first learning to deliver quality: on time, in full, every time with a definition of quality focused on the satisfaction of customer needs.
It is no coincidence that brand loyalty was stronger then than today, as 'brand' was used by customers as a proxy for quality. In this era, organisations that could reliably deliver a quality product or experience-on time, in full, every time-earned customer trust then loyalty.
By the 1980s researchers were attempting to answer the question 'what makes an organisation a good service provider' from the customers' point of view. They developed a measurement instrument, SERVQUAL, which has at its heart a 'doh' insight that is still relevant: first find out what is important to customers and then find out how you are delivering against this and fix the most important worst-performing services first.
They highlighted the gaps that exist between what organisations think are important to a good ex and how pesky customer s often disagree.
SERVQUAL consistently and almost without exception showed that customers rated reliability as the most important factor in rating a company as a quality product and service provider. Reliably keeping promises builds trust, enabling a relationship between the customer and the organisation.
Making it Easy
Reichheld's best seller, 'The Loyalty Effect' (1996) was based on research into company profitability variation in a range of industries, at a time when automation and TQM (and Six Sigma) were making improvements in how reliably organisations met customer expectations for product and service quality.
He highlighted the tremendous leverage on profit that comes to companies with the most loyal customers. These profit leaders routinely had the most loyal customers, the most loyal employees and the most loyal shareholders. The hypothesis can be summarised as:
Loyal shareholders allow management to take the long view without undue short-termism
Loyal employees get to know their customers, making it easier to transact at a personal level
Loyal customers result from the above, and they are more profitable
Reichheld's work spawned the CRM industry as companies used computers to emulate the customer memory of long term employees. Peppers and Rogers developed this hypothesis into 'l to l Marketing' the use of customer memory to mass customise experiences to ensure relevance and ease. This introduced personalisation, using data in a way that allowed even strangers to emulate good long term staff-customer relationships.(This is now called 'big data' of course!)
It seems to me that at this stage in history, Customer Experience professionals (called CRM managers at the time), had shifted emphasis to the middle layer of the pyramid, not because 'meets needs' was less important but because companies were better at it and so it was less of a differentiator. Loyalty fell as we took quality for granted, but we continued to respond to organisations which paid attention and treated us as individuals.
Personalisation goes hand in hand with ease-as minimising complexity often requires companies to dynamically adapt to individual needs and preferences. But what distinguishes personalised service from 'creepy'? Trust. So the impact of reliability remained real, just slightly more subtle.
Making it Enjoyable
Customers who take quality for granted, and quickly get used to being treated personally, now look for something more to distinguish a supplier worthy of their loyalty: an enjoyable experience they can share. If the customer experience is different and enjoyable enough they talk about it with their friends - hundreds of them because of the amplification of social media "Customers now look for an experience they can share". This has led to explicit disciplines to design the customer experience to create emotional connections, with advocacy as an objective.
Net Promoter Score, invented by Reichheld, measures how well you are doing at this level. Techniques such as customer journey mapping, which emphasises the optimisation of the personal customer experience, and gamification, which overtly introduces fun, are the tools most often applied at this apex of the pyramid.
But this type of advocacy only works if the foundation is working. Flight attendant pranks are only amusing if the plane is on time and safe. If you have destroyed customer trust with poor quality, broken promises or unfair charges... then you have destroyed the emotional foundations of advocacy.
So What?
For the customer experience professional today, this means deliverables and reporting at all three levels of the pyramid (see figure below), with rapid response procedures in place for service shortfalls at the bottom.

The Ellipsis team of Loyalty Consultants believe these strategies and systems are mandatory in what Forrester calls this 'Age of the Customer' systems that ask about:
Enjoyment & advocacy
Does dealing with us feel great?
Would you recommend us?
Ease, personalisation & minimal complexity
Do we know who you are?
Was it too hard to do business with us?
Do we reliably meet your needs?
Do you trust us?
Meeting needs, on time, in full, every time
Do we reliably meet your needs?
Do you trust us?
So today's customer experience approach is not new, but builds on the pioneering work of Deming, Reichheld et al., with scoring mechanisms to capture performance at each level of the pyramid. We must not, however, forget about the order of priority: before you build advocacy, you need to reduce unnecessary complexity, and before that, you must reliably meet customer s needs. Without this foundation, no CRM system, points program, or social media presence will bring truly loyal customers.
We are Ellipsis, the Customer Loyalty Experts. We help businesses thrive through solving complex customer problems. Please get in touch, we’d love to talk.
Download the file
Fill in the form below to gain access and download the file.